Magnetic Susceptibility
Like water, H2O2 is a diamagnetic substance (i.e., acquires an induced magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field, and tends to be expelled from an inhomogeneous field).
For anhydrous H2O2, the susceptibilities are:
k (10 °C) = -0.73 x 10-6 cgs.emu/cc
χg = -0.50 x 10-6 cgs.emu/g
χm = -17 x 10-6 cgs.emu/mole
Permeability is 1 - 9.2 x 10-6 cgs.emu/cc, or very close to that of water.
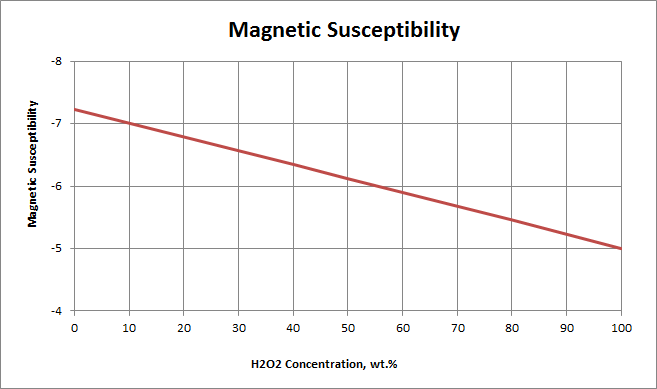
Values expressed as: χg (cgs.emu/g x 107)
Ref: A.B. Neiding and I.A. Kazarnovskii, Dokl ady Akad. Nauk S.S.S.R., 74:735 (1950) – CA 45, 1827g.